metadata
license: llama3
Arbitrary-Rating Multi-Objective Reward Model (ArmoRM) with Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) Aggregation of Reward Objectives
Authors (* indicates equal contribution)
Haoxiang Wang*, Wei Xiong*, Tengyang Xie, Han Zhao, Tong Zhang
Blog: To appear soon (with implementation details)
Tech Report: To be released in June 2024
Model: ArmoRM-Llama3-8B-v0.1
- Finetuned from model: FsfairX-LLaMA3-RM-v0.1
- Code Repository: https://github.com/RLHFlow/RLHF-Reward-Modeling/
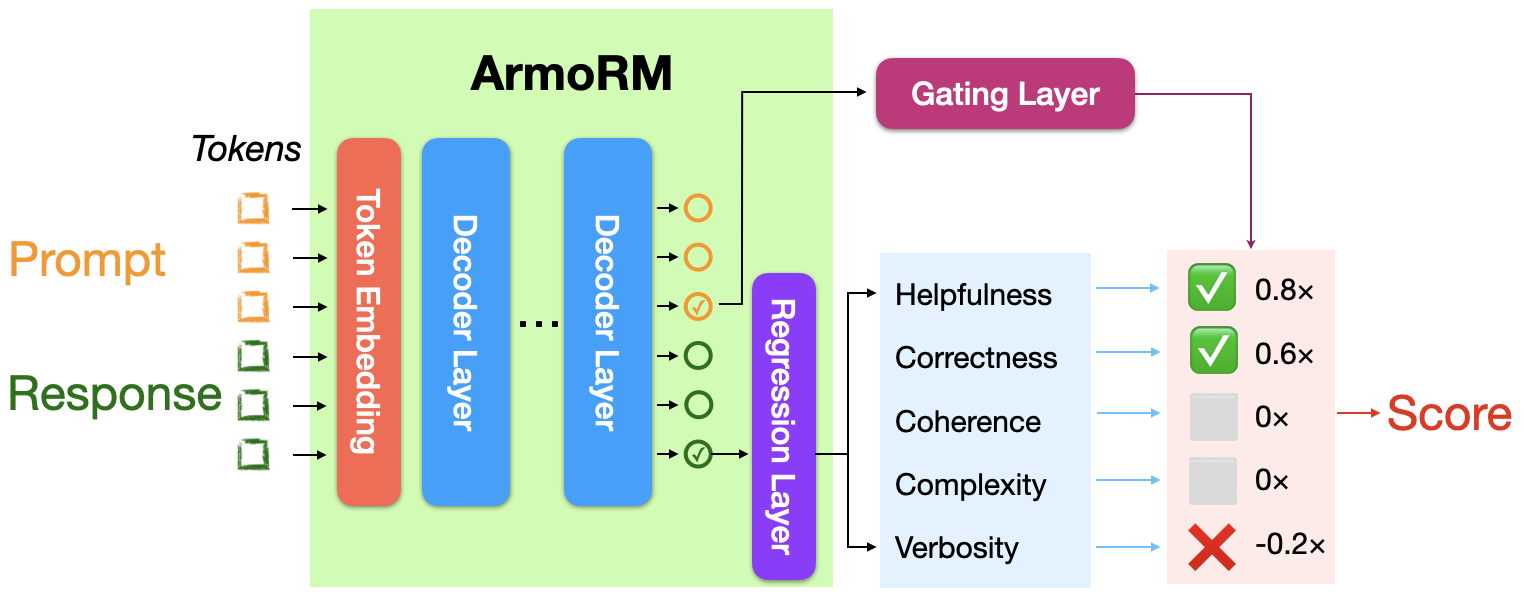
Architecture
RewardBench LeaderBoard
| Model | Base Model | Method | Score | Chat | Chat Hard | Safety | Reasoning | Prior Sets (0.5 weight) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ArmoRM-Llama3-8B-v0.1 | Llama-3 8B | ArmoRM + MoE | 88.97 | 96.9 | 76.8 | 92.2 | 97.3 | 74.3 |
| Cohere May 2024 | Unknown | Unknown | 88.25 | 96.4 | 71.3 | 92.7 | 97.7 | 78.2 |
| GPT-4 Turbo (0125 version) | GPT-4 Turbo | LLM-as-a-Judge | 84.25 | 95.3 | 74.3 | 87.2 | 86.9 | 70.9 |
| FsfairX-LLaMA3-RM-v0.1 | Llama-3 8B | Bradley-Terry | 83.61 | 99.4 | 65.1 | 87.8 | 86.4 | 74.9 |
| Starling-RM-34B | Yi-34B | Bradley-Terry | 81.44 | 96.9 | 57.2 | 88.2 | 88.5 | 71.4 |
Demo Code
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification, AutoTokenizer
device = "cuda"
path = "RLHFlow/ArmoRM-Llama3-8B-v0.1"
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(path, device_map=device,
trust_remote_code=True, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(path, use_fast=True)
# We load a random sample from the validation set of the HelpSteer dataset
prompt = 'What are some synonyms for the word "beautiful"?'
response = "Nicely, Beautifully, Handsome, Stunning, Wonderful, Gorgeous, Pretty, Stunning, Elegant"
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": prompt},
{"role": "assistant", "content": response}]
input_ids = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(input_ids)
# Multi-objective rewards for the response
multi_obj_rewards = output.rewards.cpu().float()
# The gating layer's output is conditioned on the prompt
gating_output = output.gating_output.cpu().float()
# The preference score for the response, aggregated from the
# multi-objective rewards with the gating layer
preference_score = output.score.cpu().float()
# We apply a transformation matrix to the multi-objective rewards
# before multiplying with the gating layer's output. This mainly aims
# at reducing the verbosity bias of the original reward objectives
obj_transform = model.reward_transform_matrix.data.cpu().float()
# The final coefficients assigned to each reward objective
multi_obj_coeffs = gating_output @ obj_transform.T
# The preference score is the linear combination of the multi-objective rewards with
# the multi-objective coefficients, which can be verified by the following assertion
assert torch.isclose(torch.sum(multi_obj_rewards * multi_obj_coeffs, dim=1), preference_score, atol=1e-3)
# Find the top-K reward objectives with coefficients of the highest magnitude
K = 3
top_obj_dims = torch.argsort(torch.abs(multi_obj_coeffs), dim=1, descending=True,)[:, :K]
top_obj_coeffs = torch.gather(multi_obj_coeffs, dim=1, index=top_obj_dims)
# The attributes of the 19 reward objectives
attributes = ['helpsteer-helpfulness','helpsteer-correctness','helpsteer-coherence',
'helpsteer-complexity','helpsteer-verbosity','ultrafeedback-overall_score',
'ultrafeedback-instruction_following', 'ultrafeedback-truthfulness',
'ultrafeedback-honesty','ultrafeedback-helpfulness','beavertails-is_safe',
'prometheus-score','argilla-overall_quality','argilla-judge_lm','code-complexity',
'code-style','code-explanation','code-instruction-following','code-readability']
example_index = 0
for i in range(K):
attribute = attributes[top_obj_dims[example_index, i].item()]
coeff = top_obj_coeffs[example_index, i].item()
print(f"{attribute}: {round(coeff,5)}")
# code-complexity: 0.19922
# helpsteer-verbosity: -0.10864
# ultrafeedback-instruction_following: 0.07861
# The actual rewards of this example from the HelpSteer dataset
# are [3,3,4,2,2] for the five helpsteer objectives:
# helpfulness, correctness, coherence, complexity, verbosity
# We can linearly transform our predicted rewards to the
# original reward space to compare with the ground truth
helpsteer_rewards_pred = multi_obj_rewards[0, :5] * 5 - 0.5
print(helpsteer_rewards_pred)
# [2.78125 2.859375 3.484375 1.3847656 1.296875 ]
Citation
If you find this work useful for your research, please consider citing:
@misc{wang2024interpretable,
title={Interpretable Preferences via Multi-Objective Reward Modeling and Mixture-of-Experts},
author={Wang, Haoxiang and Xiong, Wei and Xie, Tengyang and Zhao, Han and Zhang, Tong},
year={2024}
}
@inproceedings{wang2024arithmetic,
title={Arithmetic Control of LLMs for Diverse User Preferences: Directional Preference Alignment with Multi-Objective Rewards},
author={Haoxiang Wang and Yong Lin and Wei Xiong and Rui Yang and Shizhe Diao and Shuang Qiu and Han Zhao and Tong Zhang},
year={2024},
booktitle={ACL},
}
The second entry, "Arithmetic Control of LLMs for Diverse User Preferences: Directional Preference Alignment with Multi-Objective Rewards", is another recent work of ours that trained a multi-objective reward model and adopted it for LLM alignment, which motivated us to develop the current work.