Quickstart Guide
For the complete getting started tutorial series <- click here
Welcome to the Quickstart Guide! This guide will walk you through setting up, building, and running your own AutoGPT agent. Whether you're a seasoned AI developer or just starting out, this guide will provide you with the steps to jumpstart your journey in AI development with AutoGPT.
System Requirements
This project supports Linux (Debian-based), Mac, and Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). If you use a Windows system, you must install WSL. You can find the installation instructions for WSL here.
Getting Setup
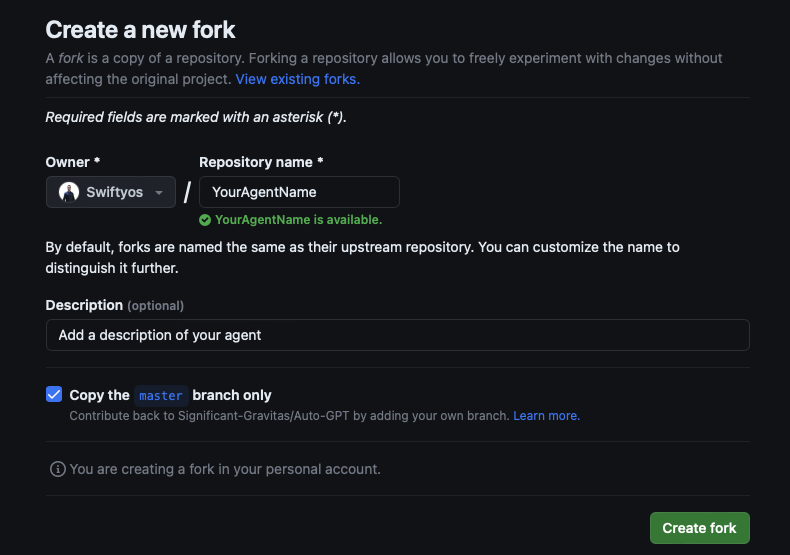
Fork the Repository To fork the repository, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the main page of the repository.
- In the top-right corner of the page, click Fork.
- On the next page, select your GitHub account to create the fork.
- Wait for the forking process to complete. You now have a copy of the repository in your GitHub account.
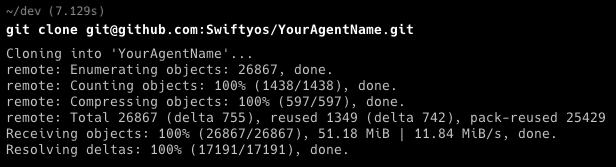
Clone the Repository To clone the repository, you need to have Git installed on your system. If you don't have Git installed, download it from here. Once you have Git installed, follow these steps:
- Open your terminal.
- Navigate to the directory where you want to clone the repository.
- Run the git clone command for the fork you just created
- Then open your project in your ide
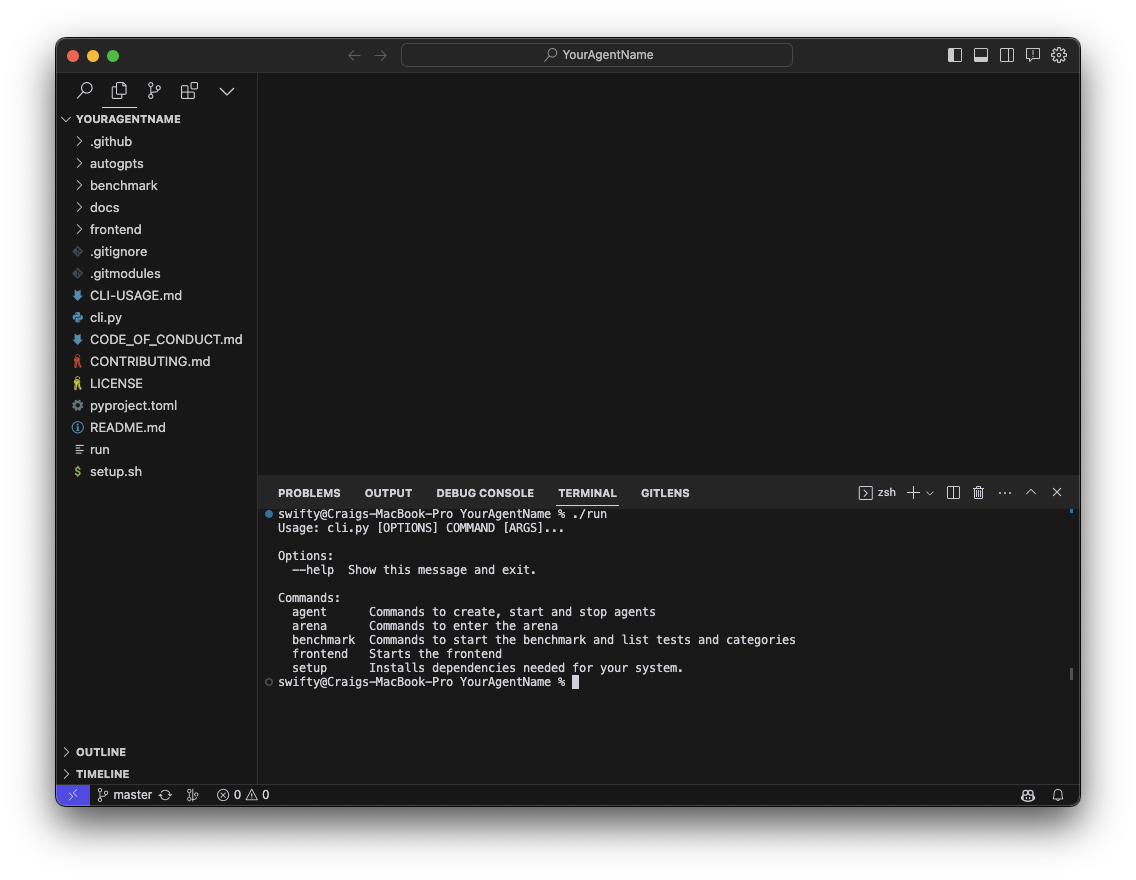
Setup the Project Next, we need to set up the required dependencies. We have a tool to help you perform all the tasks on the repo. It can be accessed by running the
runcommand by typing./runin the terminal.The first command you need to use is
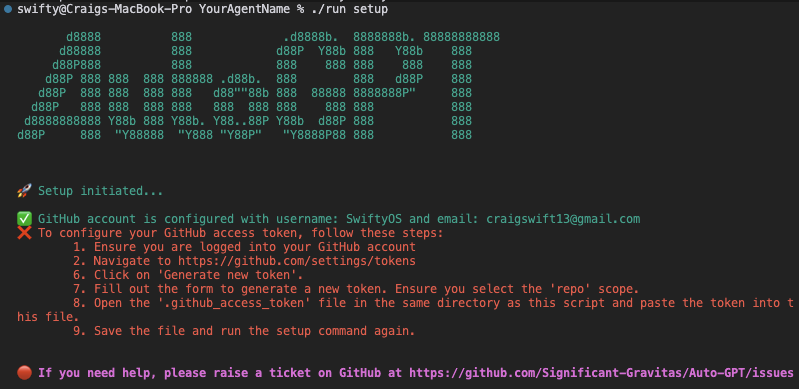
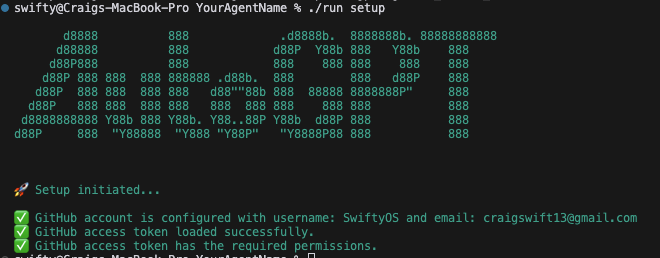
./run setup.This will guide you through setting up your system. Initially, you will get instructions for installing Flutter and Chrome and setting up your GitHub access token like the following image:
For Windows Users
If you're a Windows user and experience issues after installing WSL, follow the steps below to resolve them.
Update WSL
Run the following command in Powershell or Command Prompt:
- Enable the optional WSL and Virtual Machine Platform components.
- Download and install the latest Linux kernel.
- Set WSL 2 as the default.
- Download and install the Ubuntu Linux distribution (a reboot may be required).
wsl --install
For more detailed information and additional steps, refer to Microsoft's WSL Setup Environment Documentation.
Resolve FileNotFoundError or "No such file or directory" Errors
When you run ./run setup, if you encounter errors like No such file or directory or FileNotFoundError, it might be because Windows-style line endings (CRLF - Carriage Return Line Feed) are not compatible with Unix/Linux style line endings (LF - Line Feed).
To resolve this, you can use the dos2unix utility to convert the line endings in your script from CRLF to LF. Here’s how to install and run dos2unix on the script:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install dos2unix
dos2unix ./run
After executing the above commands, running ./run setup should work successfully.
Store Project Files within the WSL File System
If you continue to experience issues, consider storing your project files within the WSL file system instead of the Windows file system. This method avoids path translations and permissions issues and provides a more consistent development environment.
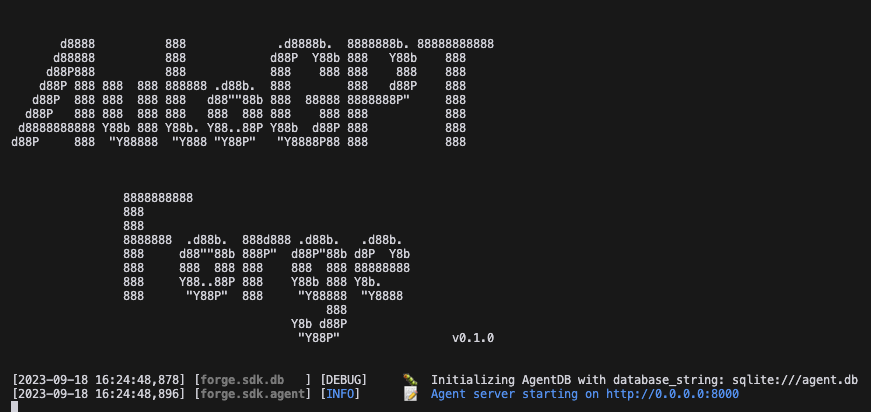
You can keep running the command to get feedback on where you are up to with your setup. When setup has been completed, the command will return an output like this:
Creating Your Agent
After completing the setup, the next step is to create your agent template.
Execute the command ./run agent create YOUR_AGENT_NAME, where YOUR_AGENT_NAME should be replaced with your chosen name.
Tips for naming your agent:
- Give it its own unique name, or name it after yourself
- Include an important aspect of your agent in the name, such as its purpose
Examples: SwiftyosAssistant, PwutsPRAgent, MySuperAgent
Running your Agent
Your agent can be started using the command: ./run agent start YOUR_AGENT_NAME
This starts the agent on the URL: http://localhost:8000/
The front end can be accessed from http://localhost:8000/; first, you must log in using either a Google account or your GitHub account.
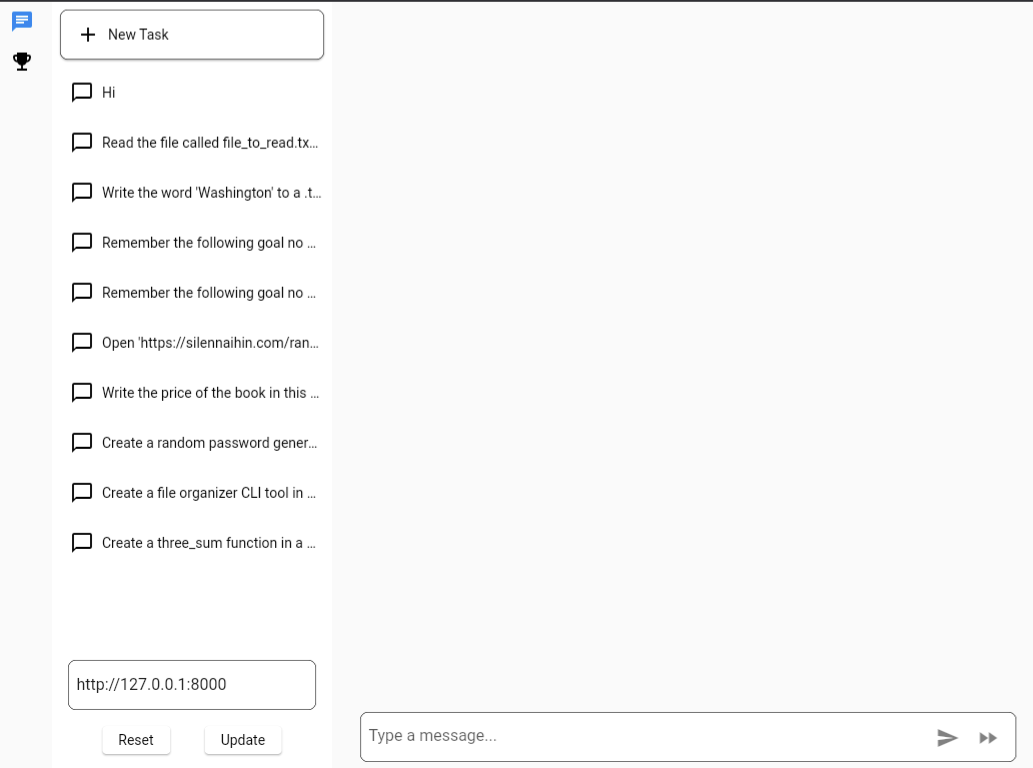
Upon logging in, you will get a page that looks something like this: your task history down the left-hand side of the page, and the 'chat' window to send tasks to your agent.
When you have finished with your agent or just need to restart it, use Ctl-C to end the session. Then, you can re-run the start command.
If you are having issues and want to ensure the agent has been stopped, there is a ./run agent stop command, which will kill the process using port 8000, which should be the agent.
Benchmarking your Agent
The benchmarking system can also be accessed using the CLI too:
agpt % ./run benchmark
Usage: cli.py benchmark [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
Commands to start the benchmark and list tests and categories
Options:
--help Show this message and exit.
Commands:
categories Benchmark categories group command
start Starts the benchmark command
tests Benchmark tests group command
agpt % ./run benchmark categories
Usage: cli.py benchmark categories [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
Benchmark categories group command
Options:
--help Show this message and exit.
Commands:
list List benchmark categories command
agpt % ./run benchmark tests
Usage: cli.py benchmark tests [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
Benchmark tests group command
Options:
--help Show this message and exit.
Commands:
details Benchmark test details command
list List benchmark tests command
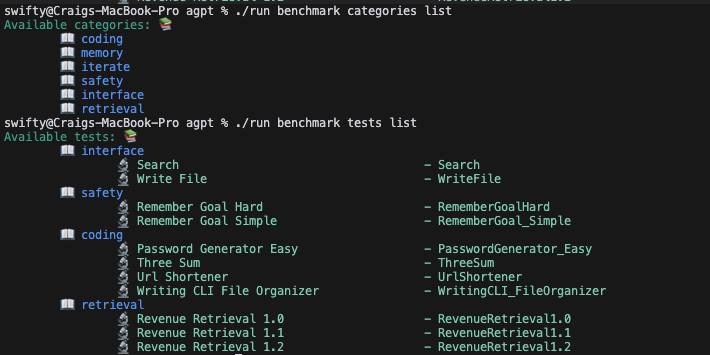
The benchmark has been split into different categories of skills you can test your agent on. You can see what categories are available with
./run benchmark categories list
# And what tests are available with
./run benchmark tests list
Finally, you can run the benchmark with
./run benchmark start YOUR_AGENT_NAME