import pandas as pd
import streamlit as st
import streamlit_ace as stace
import duckdb
import numpy as np # for user session
import scipy # for user session
import plotly.express as px # for user session
import plotly.figure_factory as ff # for user session
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # for user session
import sklearn
from ydata_profiling import ProfileReport
from streamlit_pandas_profiling import st_profile_report
st.set_page_config(page_title="PySQLify", page_icon="🔎", layout="wide")
st.title("PySQLify")
st.write("_Data Analysis_ Tool")
p = st.write
print = st.write
@st.cache
def _read_csv(f, **kwargs):
df = pd.read_csv(f, on_bad_lines="skip", **kwargs)
# clean
df.columns = [c.strip() for c in df.columns]
return df
SAMPLE_DATA = {
"Churn dataset": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AtashfarazNavid/MachineLearing-ChurnModeling/main/Streamlit-WebApp-1/Churn.csv",
"Periodic Table": "https://gist.githubusercontent.com/GoodmanSciences/c2dd862cd38f21b0ad36b8f96b4bf1ee/raw/1d92663004489a5b6926e944c1b3d9ec5c40900e/Periodic%2520Table%2520of%2520Elements.csv",
"Movies": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/reisanar/datasets/master/HollywoodMovies.csv",
"Iris Flower": "https://gist.githubusercontent.com/netj/8836201/raw/6f9306ad21398ea43cba4f7d537619d0e07d5ae3/iris.csv",
"World Population": "https://gist.githubusercontent.com/curran/13d30e855d48cdd6f22acdf0afe27286/raw/0635f14817ec634833bb904a47594cc2f5f9dbf8/worldcities_clean.csv",
"Country Table": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/datasciencedojo/datasets/master/WorldDBTables/CountryTable.csv",
"World Cities": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dr5hn/countries-states-cities-database/master/csv/cities.csv",
"World States": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dr5hn/countries-states-cities-database/master/csv/states.csv",
"World Countries": "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dr5hn/countries-states-cities-database/master/csv/countries.csv"
}
def read_data():
txt = "Upload a data file (supported files: .csv)"
placeholder = st.empty()
with placeholder:
col1, col2, col3 = st.columns([3, 2, 1])
with col1:
file_ = st.file_uploader(txt, help="TODO: .tsv, .xls, .xlsx")
with col2:
url = st.text_input(
"Read from a URL",
placeholder="Enter URL (supported types: .csv and .tsv)",
)
if url:
file_ = url
with col3:
selected = st.selectbox("Select a sample dataset", options=[""] + list(SAMPLE_DATA))
if selected:
file_ = SAMPLE_DATA[selected]
if not file_:
st.stop()
placeholder.empty()
kwargs = {"skiprows": st.number_input("skip header", value=0, max_value=10)}
try:
return _read_csv(file_, **kwargs)
except Exception as e:
st.warning("Unsupported file type!")
st.stop()
def display(df):
view_info = st.checkbox("view data types")
st.dataframe(df, use_container_width=True)
# info
st.markdown(f"> shape `{df.shape}`", unsafe_allow_html=True)
if view_info:
types_ = df.dtypes.to_dict()
types_ = [{"Column": c, "Type": t} for c, t in types_.items()]
df_ = pd.DataFrame(types_)
st.sidebar.subheader("TABLE DETAILS")
st.sidebar.write(df_)
def code_editor(language, hint, show_panel, key=None):
# Spawn a new Ace editor
placeholder = st.empty()
default_theme = "solarized_dark" if language == "sql" else "chrome"
with placeholder.expander("CELL CONFIG"):
# configs
_THEMES = stace.THEMES
_KEYBINDINGS = stace.KEYBINDINGS
col21, col22 = st.columns(2)
with col21:
theme = st.selectbox("Theme", options=[default_theme] + _THEMES, key=f"{language}1{key}")
tab_size = st.slider("Tab size", min_value=1, max_value=8, value=4, key=f"{language}2{key}")
with col22:
keybinding = st.selectbox("Keybinding", options=[_KEYBINDINGS[-2]] + _KEYBINDINGS, key=f"{language}3{key}")
font_size = st.slider("Font size", min_value=5, max_value=24, value=14, key=f"{language}4{key}")
height = st.slider("Editor height", value=230, max_value=777,key=f"{language}5{key}")
# kwargs = {theme: theme, keybinding: keybinding} # TODO: DRY
if not show_panel:
placeholder.empty()
content = stace.st_ace(
language=language,
height=height,
show_gutter=False,
# annotations="",
placeholder=hint,
keybinding=keybinding,
theme=theme,
font_size=font_size,
tab_size=tab_size,
key=key
)
# Display editor's content as you type
# content
return content
@st.cache
def query_data(sql, df):
try:
return duckdb.query(sql).df()
except Exception as e:
st.warning("Invalid Query!")
# st.stop()
def download(df, key, save_as="results.csv"):
# -- to download
# @st.cache_data
def convert_df(_df):
return _df.to_csv().encode("utf-8")
csv = convert_df(df)
st.download_button(
"Download",
csv,
save_as,
"text/csv",
key=key
)
def display_results(query: str, result: pd.DataFrame, key: str):
st.dataframe(result, use_container_width=True)
st.markdown(f"> `{result.shape}`")
download(result, key=key)
def run_python_script(user_script, key):
if user_script.startswith("st.") or ";" in user_script:
py = user_script
elif user_script.endswith("?"): # -- same as ? in Jupyter Notebook
in_ = user_script.replace("?", "")
py = f"st.help({in_})"
else:
py = f"st.write({user_script})"
try:
cmds = py.split(";")
for cmd in cmds:
exec(cmd)
except Exception as e:
c1, c2 = st.columns(2)
c1.warning("Wrong Python command.")
if c2.button("Show error", key=key):
st.exception(e)
@st.experimental_singleton
def data_profiler(df):
return ProfileReport(df, title="Profiling Report")
def docs():
content = """
# What
Upload a dataset to process (manipulate/analyze) it using SQL and Python, similar to running Jupyter Notebooks.
To get started, drag and drop the dataset file, read from a URL, or select a sample dataset. To load a new dataset, refresh the webpage.
> [_src code_ here](https://github.com/iamaziz/sqlify)
More public datasets available [here](https://github.com/fivethirtyeight/data).
# Usage
Example usage
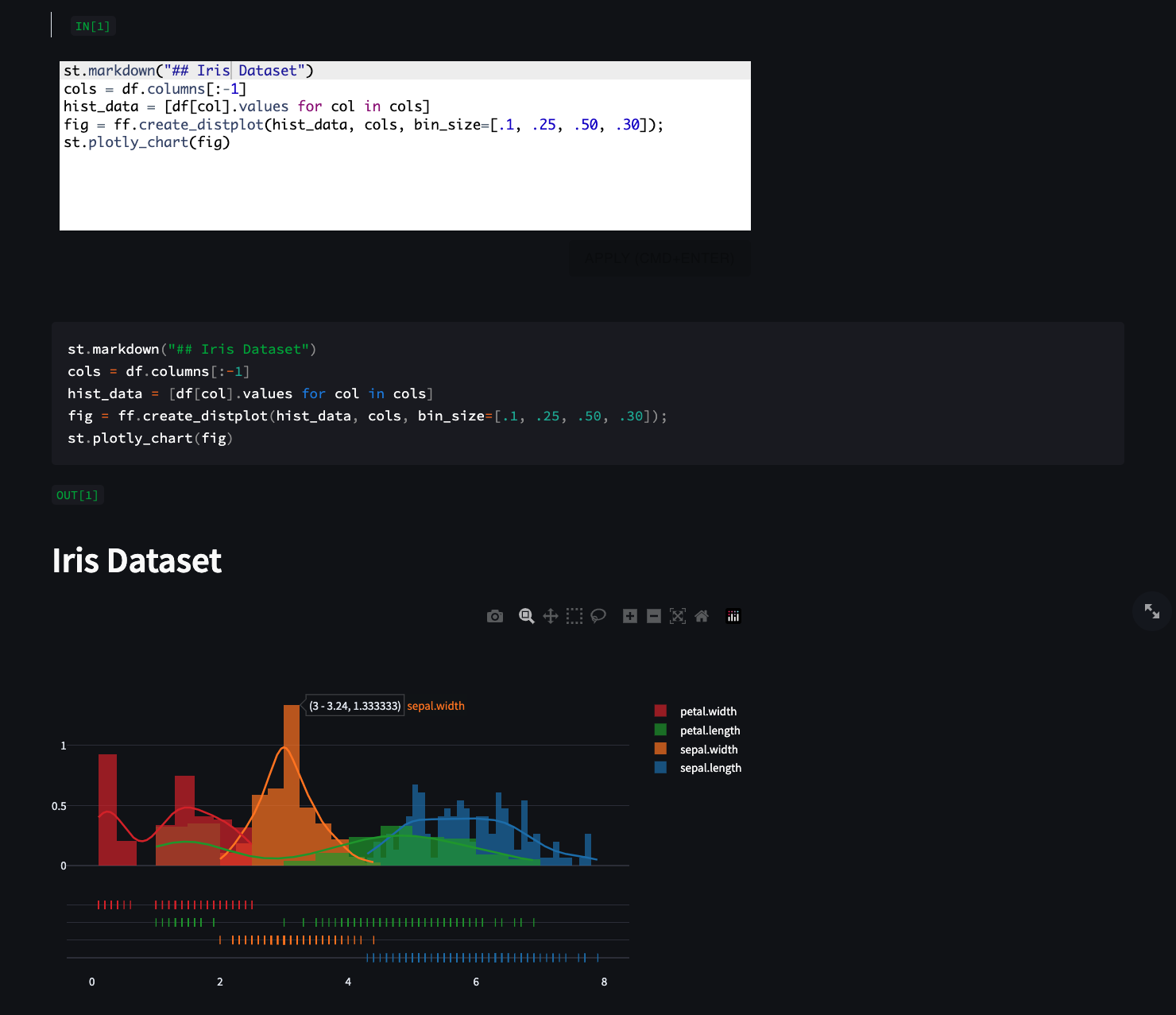
> After loading the sample Iris dataset from sklearn (or select it from the dropdown list), the lines below can be executed inside a Python cell:
```python
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris;
from sklearn import tree;
iris = load_iris();
X, y = iris.data, iris.target;
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=4);
clf = clf.fit(X, y);
plt.figure(figsize=(7,3));
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
tree.plot_tree(clf, filled=True, fontsize=4);
st.pyplot(fig)
```
Which outputs the tree below:
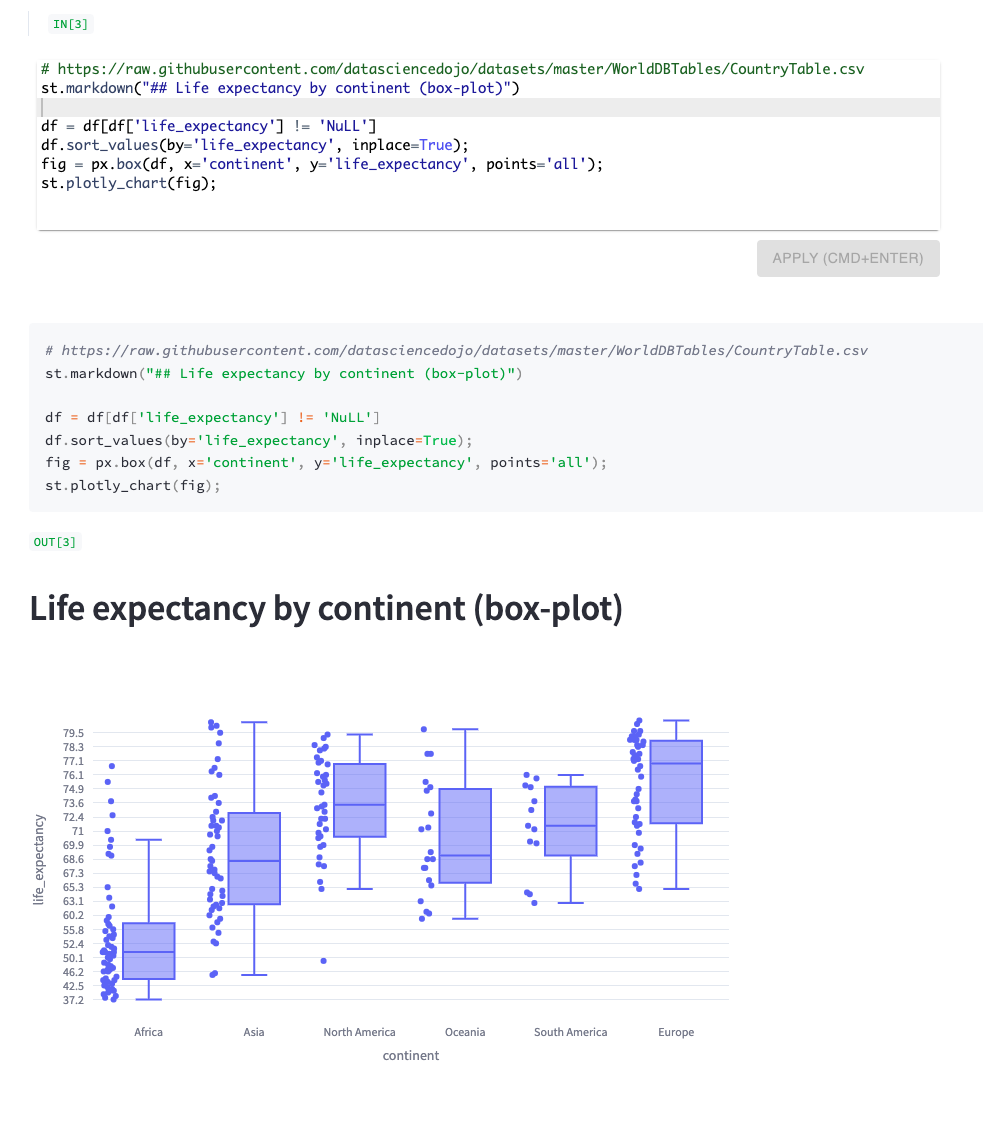
>  # SCREENSHOTS
## _EXAMPLE 1_
## _EXAMPLE 2_
## _EXAMPLE 3_
## _EXAMPLE 4_
"""
with st.expander("READE"):
st.markdown(content, unsafe_allow_html=True)
return st.checkbox("Show more code examples")
def display_example_snippets():
from glob import glob
examples = glob("./examples/*")
with st.expander("EXAMPLES"):
example = st.selectbox("", options=[""] + examples)
if example:
with open(example, "r") as f:
content = f.read()
st.code(content)
if __name__ == "__main__":
show_examples = docs()
if show_examples:
display_example_snippets()
df = read_data()
display(df)
# run and execute SQL script
def sql_cells(df):
st.write("---")
st.header("SQL")
hint = """Type SQL to query the loaded dataset, data is stored in a table named 'df'.
For example, to select 10 rows:
SELECT * FROM df LIMIT 10
Describe the table:
DESCRIBE TABLE df
"""
number_cells = st.sidebar.number_input("Number of SQL cells to use", value=1, max_value=40)
for i in range(number_cells):
col1, col2 = st.columns([2, 1])
st.markdown("
# SCREENSHOTS
## _EXAMPLE 1_

## _EXAMPLE 2_


## _EXAMPLE 3_

## _EXAMPLE 4_

"""
with st.expander("READE"):
st.markdown(content, unsafe_allow_html=True)
return st.checkbox("Show more code examples")
def display_example_snippets():
from glob import glob
examples = glob("./examples/*")
with st.expander("EXAMPLES"):
example = st.selectbox("", options=[""] + examples)
if example:
with open(example, "r") as f:
content = f.read()
st.code(content)
if __name__ == "__main__":
show_examples = docs()
if show_examples:
display_example_snippets()
df = read_data()
display(df)
# run and execute SQL script
def sql_cells(df):
st.write("---")
st.header("SQL")
hint = """Type SQL to query the loaded dataset, data is stored in a table named 'df'.
For example, to select 10 rows:
SELECT * FROM df LIMIT 10
Describe the table:
DESCRIBE TABLE df
"""
number_cells = st.sidebar.number_input("Number of SQL cells to use", value=1, max_value=40)
for i in range(number_cells):
col1, col2 = st.columns([2, 1])
st.markdown("
", unsafe_allow_html=True)
col1.write(f"> `IN[{i+1}]`")
show_panel = col2.checkbox("Show cell config panel", key=f"sql_{i}")
key = f"sql{i}"
sql = code_editor("sql", hint, show_panel=show_panel, key=key)
if sql:
st.code(sql, language="sql")
st.write(f"`OUT[{i+1}]`")
res = query_data(sql, df)
display_results(sql, res, f"{key}{sql}")
# run and dexectue python script
def python_cells():
st.write("---")
st.header("Python")
hint = """Type Python command (one-liner) to execute or manipulate the dataframe e.g. `df.sample(7)`. By default, results are rendered using `st.write()`.
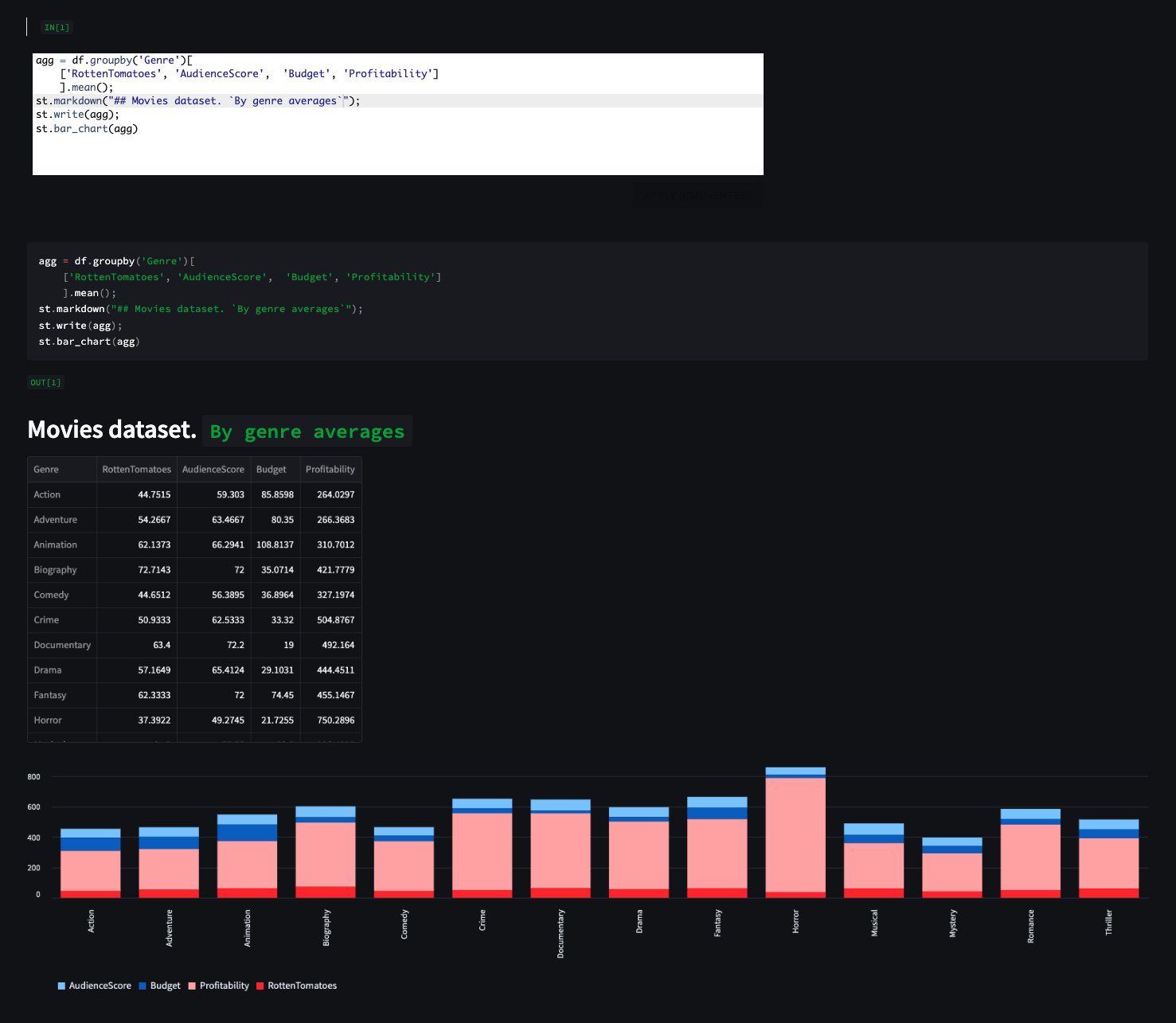
📊 Visulaization example: from "movies" dataset, plot average rating by genre:
st.line_chart(df.groupby("Genre")[["RottenTomatoes", "AudienceScore"]].mean())
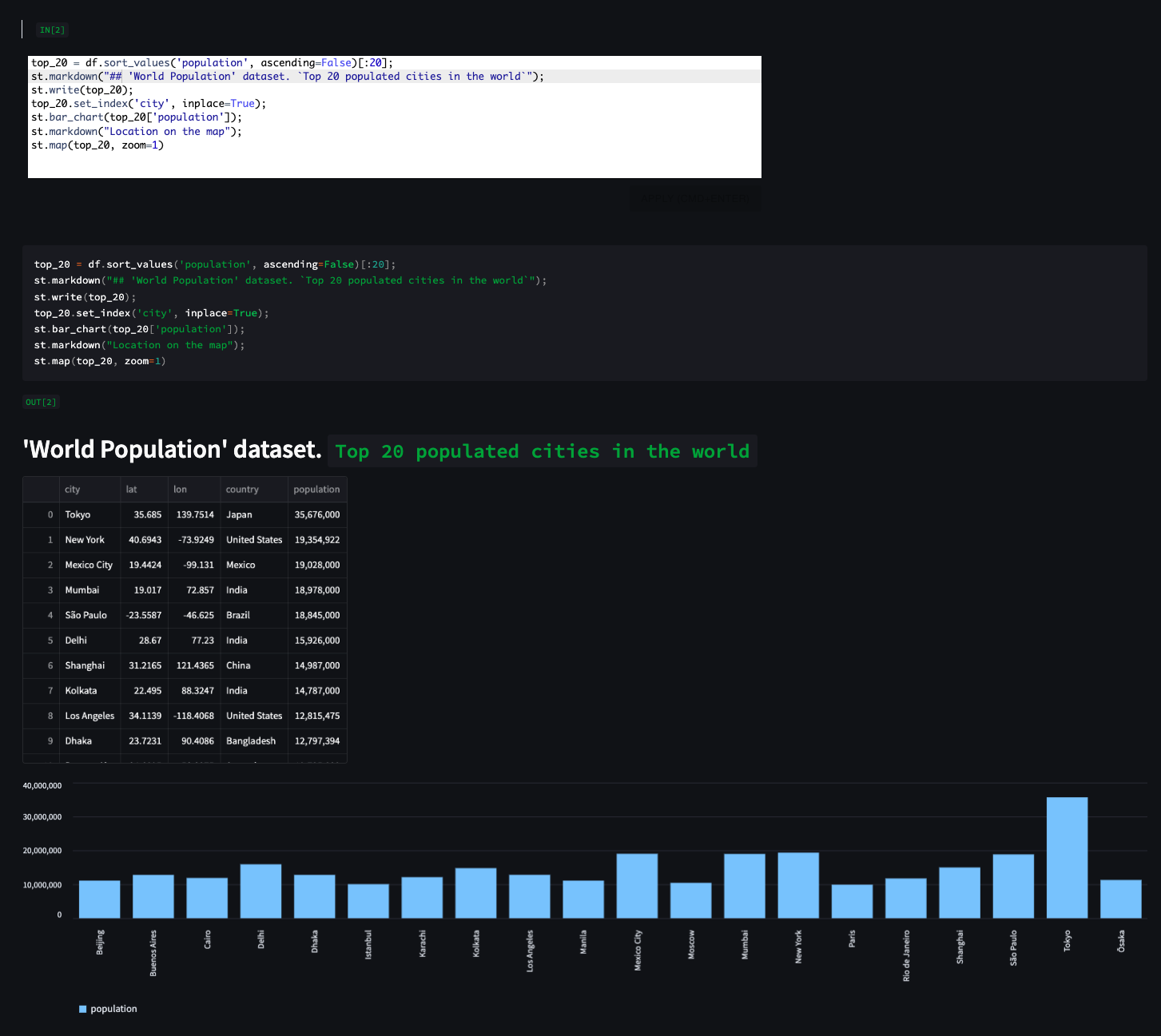
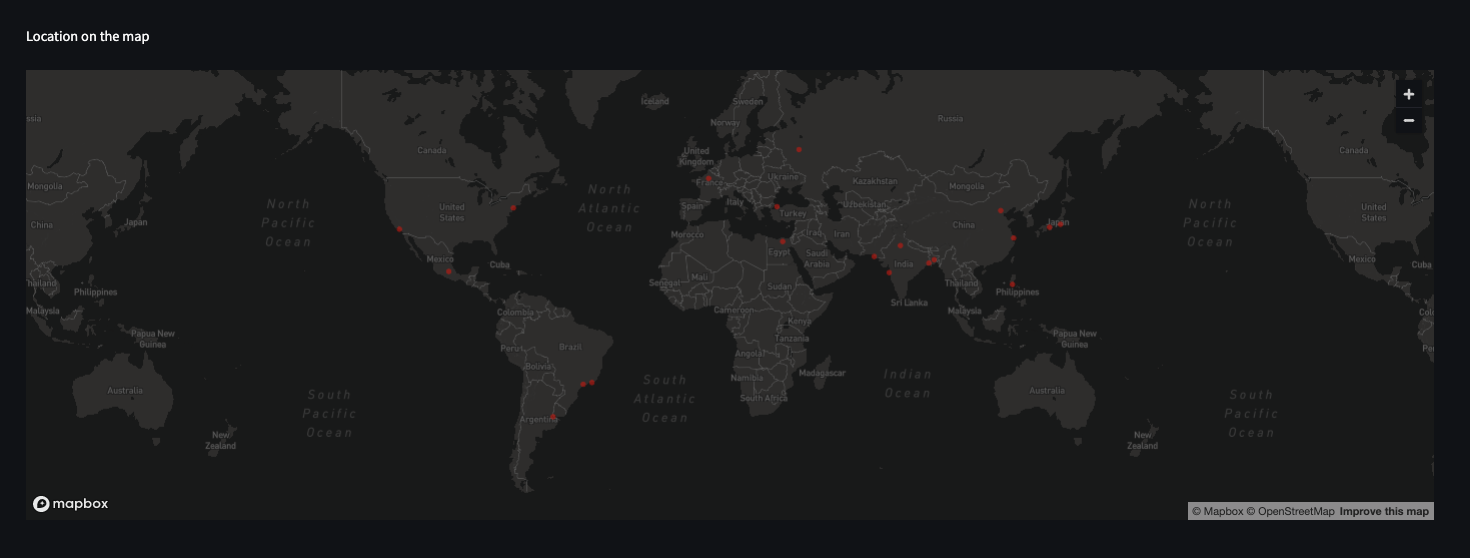
🗺 Maps example: show the top 10 populated cities in the world on map (from "Cities Population" dataset)
st.map(df.sort_values(by='population', ascending=False)[:10])
NOTE: for multi-lines, a semi-colon can be used to end each line e.g.
print("first line");
print("second line);
"""
help = """
For multiple lines, use semicolons e.g.
```python
fig, ax = plt.subplots();
ax.hist(df[[col1, col2]]);
st.pyplot(fig);
```
or
```python
groups = [group for _, group in df.groupby('class')];
for i in range(3):
st.write(groups[i]['name'].iloc[0])
st.bar_chart(groups[i].mean())
```
"""
number_cells = st.sidebar.number_input("Number of Python cells to use", value=1, max_value=40, min_value=1, help=help)
for i in range(number_cells):
st.markdown("
", unsafe_allow_html=True)
col1, col2 = st.columns([2, 1])
col1.write(f"> `IN[{i+1}]`")
show_panel = col2.checkbox("Show cell config panel", key=f"panel{i}")
user_script = code_editor("python", hint, show_panel=show_panel, key=i)
if user_script:
df.rename(columns={"lng": "lon"}, inplace=True) # hot-fix for "World Population" dataset
st.code(user_script, language="python")
st.write(f"`OUT[{i+1}]`")
run_python_script(user_script, key=f"{user_script}{i}")
if st.sidebar.checkbox("Show SQL cells", value=True):
sql_cells(df)
if st.sidebar.checkbox("Show Python cells", value=True):
python_cells()
st.sidebar.write("---")
if st.sidebar.checkbox("Generate Data Profile Report", help="pandas profiling, generated by [ydata-profiling](https://github.com/ydataai/ydata-profiling)"):
st.write("---")
st.header("Data Profiling")
profile = data_profiler(df)
st_profile_report(profile)
st.write("---") # SCREENSHOTS
## _EXAMPLE 1_

## _EXAMPLE 2_


## _EXAMPLE 3_

## _EXAMPLE 4_

"""
with st.expander("READE"):
st.markdown(content, unsafe_allow_html=True)
return st.checkbox("Show more code examples")
def display_example_snippets():
from glob import glob
examples = glob("./examples/*")
with st.expander("EXAMPLES"):
example = st.selectbox("", options=[""] + examples)
if example:
with open(example, "r") as f:
content = f.read()
st.code(content)
if __name__ == "__main__":
show_examples = docs()
if show_examples:
display_example_snippets()
df = read_data()
display(df)
# run and execute SQL script
def sql_cells(df):
st.write("---")
st.header("SQL")
hint = """Type SQL to query the loaded dataset, data is stored in a table named 'df'.
For example, to select 10 rows:
SELECT * FROM df LIMIT 10
Describe the table:
DESCRIBE TABLE df
"""
number_cells = st.sidebar.number_input("Number of SQL cells to use", value=1, max_value=40)
for i in range(number_cells):
col1, col2 = st.columns([2, 1])
st.markdown("
# SCREENSHOTS
## _EXAMPLE 1_

## _EXAMPLE 2_


## _EXAMPLE 3_

## _EXAMPLE 4_

"""
with st.expander("READE"):
st.markdown(content, unsafe_allow_html=True)
return st.checkbox("Show more code examples")
def display_example_snippets():
from glob import glob
examples = glob("./examples/*")
with st.expander("EXAMPLES"):
example = st.selectbox("", options=[""] + examples)
if example:
with open(example, "r") as f:
content = f.read()
st.code(content)
if __name__ == "__main__":
show_examples = docs()
if show_examples:
display_example_snippets()
df = read_data()
display(df)
# run and execute SQL script
def sql_cells(df):
st.write("---")
st.header("SQL")
hint = """Type SQL to query the loaded dataset, data is stored in a table named 'df'.
For example, to select 10 rows:
SELECT * FROM df LIMIT 10
Describe the table:
DESCRIBE TABLE df
"""
number_cells = st.sidebar.number_input("Number of SQL cells to use", value=1, max_value=40)
for i in range(number_cells):
col1, col2 = st.columns([2, 1])
st.markdown("